Causal Effects of Antibiotic Use on Resistance
Researchers: Dr. Daniel Nevo (Statistics), Dr. Uri Obolski (Public Health)
Researchers: Dr. Daniel Nevo (Statistics), Dr. Uri Obolski (Public Health)
Antibiotic resistance of bacterial infections is a major public health threat. When a patient is presented with a bacterial infection, there is a built-in uncertainty in a doctor’s decision of prescribing antibiotics before laboratory confirmed results are available.
A key piece of information is missing in this decision-making process - a quantitative estimate of the causal effect of antibiotics on future antibiotic resistance of bacterial infections.
We apply advanced causal inference and machine learning methods to a highly detailed dataset of electronic medical records of over 40,000 Israeli hospitalized patients with bacterial infections.
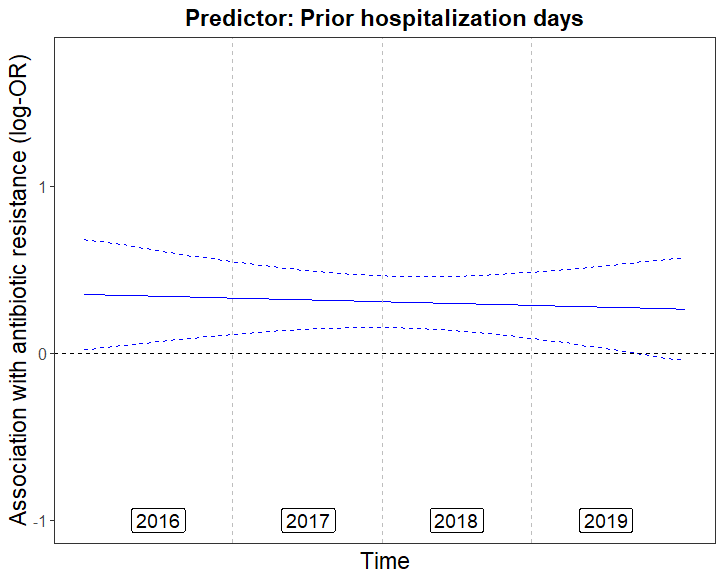
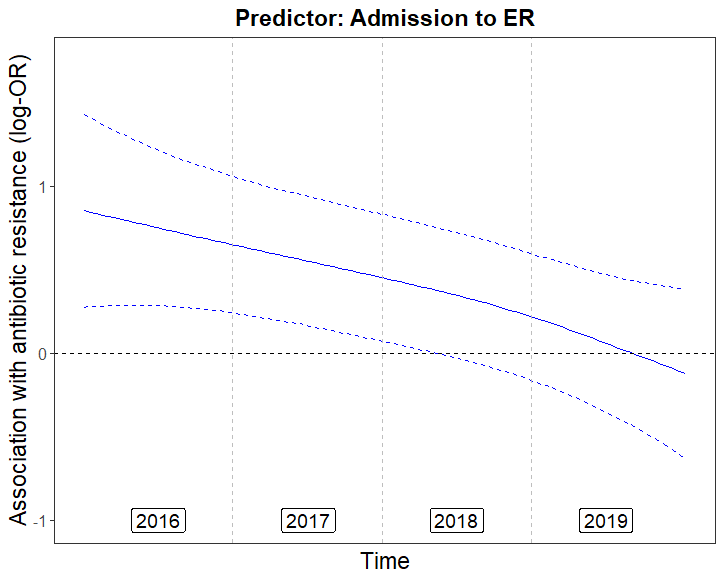
Antibiotic resistance frequencies are dynamic and constantly changing due to the rapid evolutionary response of bacteria to environmental and individual-level changes.
Our first step towards understanding this time-varying system is to identify predictors with constant effect on antibiotic resistance across time, despite the dynamic nature of the system. These predictors are themselves causal, or are surrogates of stable causal relationships.